This function mimics parts of the LiMM-PCA framework, combining ASCA+ and linear mixed models to analyse high-dimensional designed data. The default is to use REML estimation and scaling of the backprojected errors. See examples for alternatives.
Usage
limmpca(
formula,
data,
pca.in = 5,
aug_error = 0.05,
use_ED = FALSE,
REML = TRUE,
contrasts = "contr.sum",
permute = FALSE,
perm.type = c("approximate", "exact"),
SStype = "III",
...
)Arguments
- formula
Model formula accepting a single response (block) and predictors. See Details for more information.
- data
The data set to analyse.
- pca.in
Compress response before ASCA (number of components), default = 5.
- aug_error
Error term of model ("denominator", "residual", numeric alpha-value). The latter implies the first with a scaling factor.
- use_ED
Use Effective Dimensions instead of degrees of freedom when scaling.
- REML
Use restricted maximum likelihood estimation. Alternatives: TRUE (default), FALSE (ML), NULL (least squares).
- contrasts
Effect coding: "sum" (default = sum-coding), "weighted", "reference", "treatment".
- permute
Number of permutations to perform (default = 1000).
- perm.type
Type of permutation to perform, either "approximate" or "exact" (default = "approximate").
- SStype
Type of sum-of-squares: "I" = sequential, "II" = last term, obeying marginality, "III" (default) = last term, not obeying marginality.
- ...
Additional arguments to
hdanova.
Details
The Sum of Squares for the model is dependent on the SStype of the model. For SStype = "I" and SStype = "II" the SSQ is based on LLR (possibly inflating large contributions), while it is directly estimated from the model for SStype = "III". SStype = "III" is the default for LiMM-PCA and should be combined with sum coding. Sum of Squares for the random effects are based on the variance components.
References
Martin, M. and Govaerts, B. (2020). LiMM-PCA: Combining ASCA+ and linear mixed models to analyse high-dimensional designed data. Journal of Chemometrics, 34(6), e3232.
See also
Main methods: asca, apca, limmpca, msca, pcanova, prc and permanova.
Workhorse function underpinning most methods: hdanova.
Extraction of results and plotting: asca_results, asca_plots, pcanova_results and pcanova_plots
Examples
# Load candies data
data(candies)
# Default LiMM-PCA model with two factors and interaction, 5 PCA components
mod <- limmpca(assessment ~ candy*r(assessor), data=candies)
summary(mod)
#> LiMM-PCA fitted using 'lmm' (Linear Mixed Model)
#> - SS type III, sum coding, restricted model, REML estimation
#> Sum.Sq. Expl.var.(%)
#> candy 33394.40 78.00
#> candy:assessor 1192.09 2.78
#> assessor 968.07 2.26
#> Residuals 7257.45 16.95
scoreplot(mod, factor = "candy")
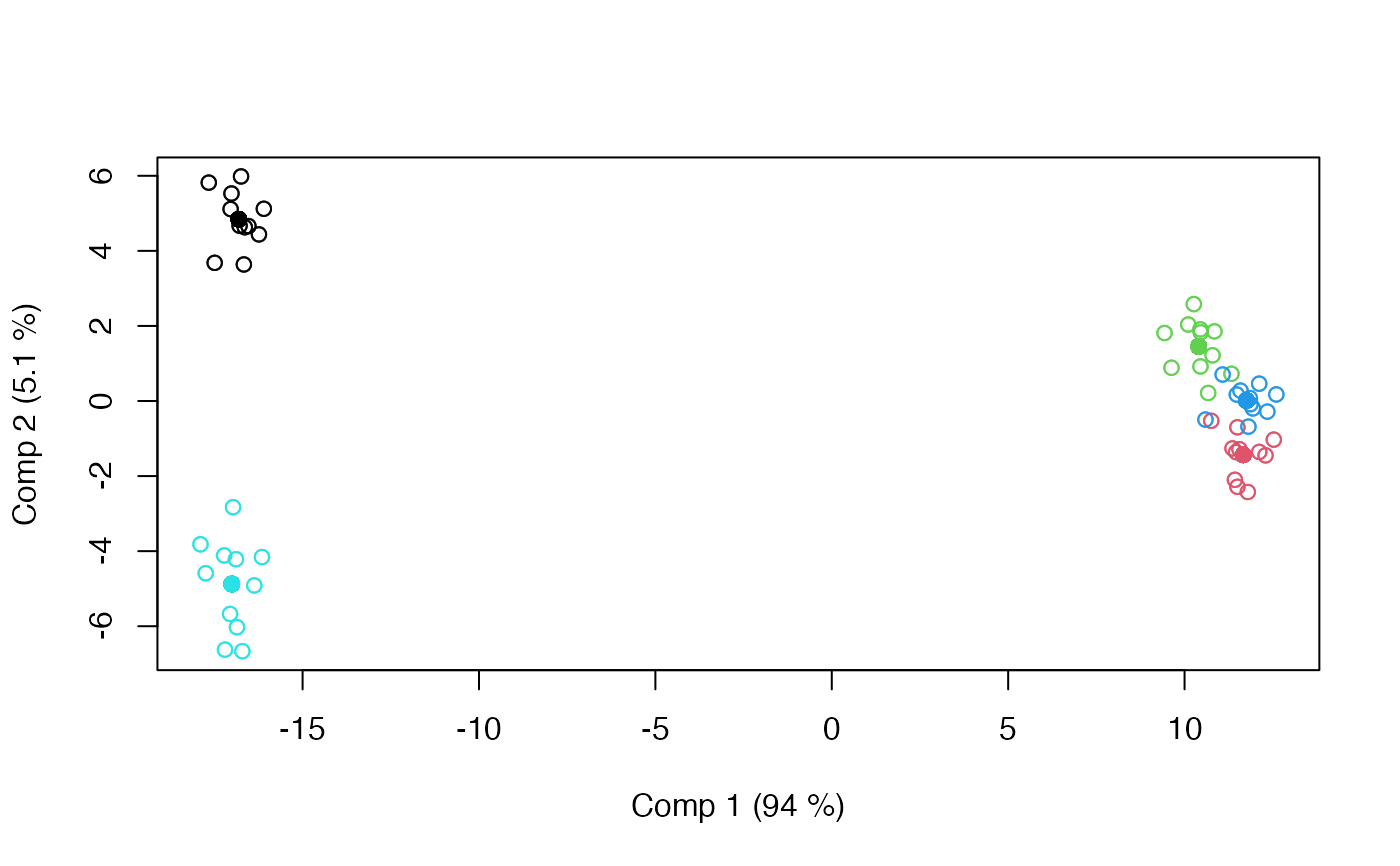 # LiMM-PCA with least squares estimation and 8 PCA components
modLS <- limmpca(assessment ~ candy*r(assessor), data=candies, REML=NULL, pca.in=8)
summary(modLS)
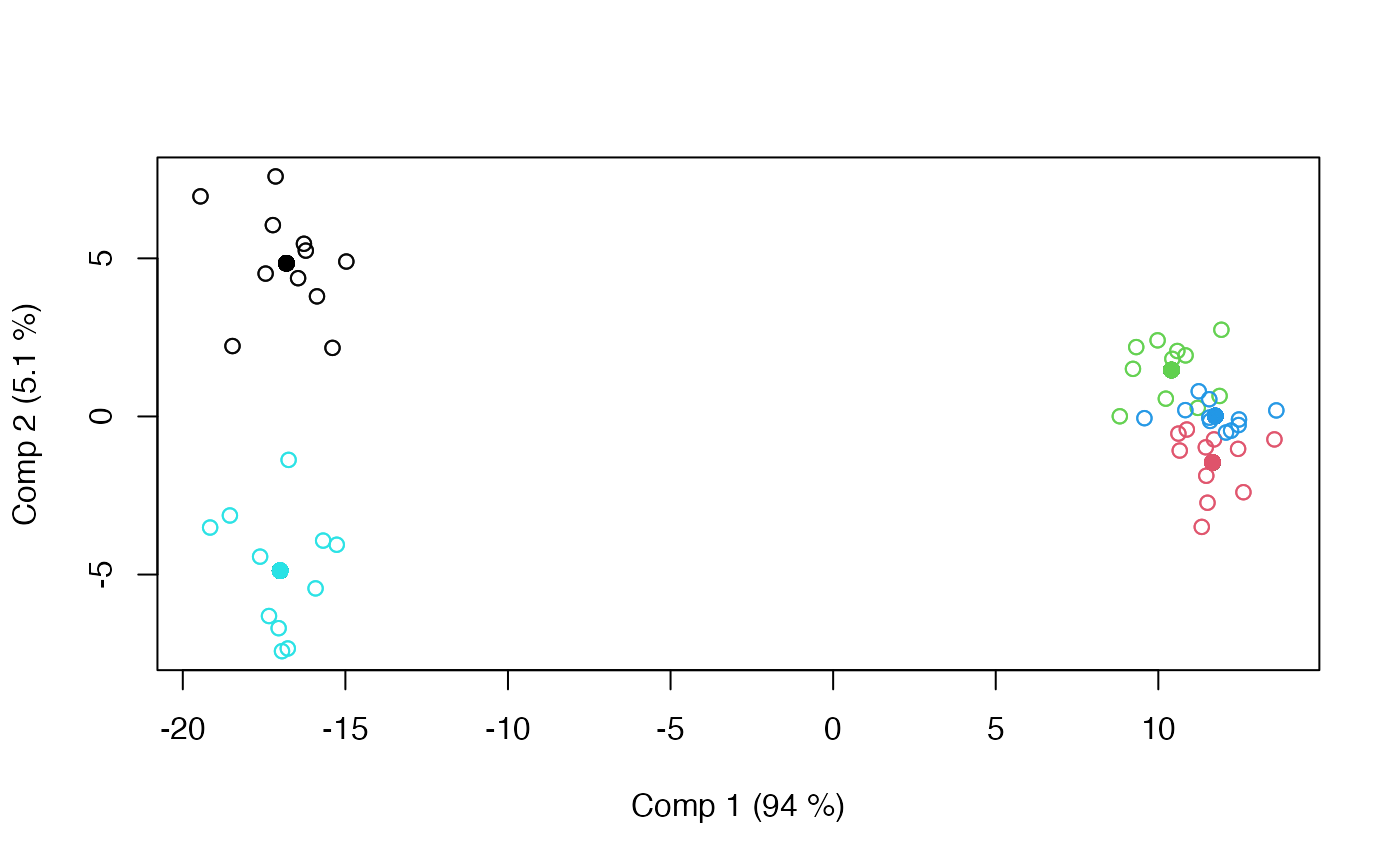
#> LiMM-PCA fitted using 'lmm' (Linear Mixed Model)
#> - SS type III, sum coding, restricted model, least squares estimation
#> Sum.Sq. Expl.var.(%)
#> candy 33415.98 74.73
#> assessor 1948.75 4.36
#> candy:assessor 3419.04 7.65
#> Residuals 5934.46 13.27
scoreplot(modLS, factor = "candy")
# LiMM-PCA with least squares estimation and 8 PCA components
modLS <- limmpca(assessment ~ candy*r(assessor), data=candies, REML=NULL, pca.in=8)
summary(modLS)
#> LiMM-PCA fitted using 'lmm' (Linear Mixed Model)
#> - SS type III, sum coding, restricted model, least squares estimation
#> Sum.Sq. Expl.var.(%)
#> candy 33415.98 74.73
#> assessor 1948.75 4.36
#> candy:assessor 3419.04 7.65
#> Residuals 5934.46 13.27
scoreplot(modLS, factor = "candy")
 # Load Caldana data
data(caldana)
# Combining effects in LiMM-PCA (assuming light is a random factor)
mod.comb <- limmpca(compounds ~ time + comb(r(light) + r(time:light)), data=caldana, pca.in=8)
summary(mod.comb)
#> LiMM-PCA fitted using 'lmm' (Linear Mixed Model)
#> - SS type III, sum coding, restricted model, REML estimation
#> Sum.Sq. Expl.var.(%)
#> time 129.51 11.20
#> light+time:light 104.85 9.07
#> Residuals 922.11 79.74
# Load Caldana data
data(caldana)
# Combining effects in LiMM-PCA (assuming light is a random factor)
mod.comb <- limmpca(compounds ~ time + comb(r(light) + r(time:light)), data=caldana, pca.in=8)
summary(mod.comb)
#> LiMM-PCA fitted using 'lmm' (Linear Mixed Model)
#> - SS type III, sum coding, restricted model, REML estimation
#> Sum.Sq. Expl.var.(%)
#> time 129.51 11.20
#> light+time:light 104.85 9.07
#> Residuals 922.11 79.74